Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Carter, L. M.*; Crawford, T. M.*; 佐藤 達彦; 古田 琢哉; Choi, C.*; Kim, C. H.*; Brown, J. L.*; Bolch, W. E.*; Zanzonico, P. B.*; Lewis, J. S.*
Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 60(12), p.1802 - 1811, 2019/12
被引用回数:22 パーセンタイル:79.81(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging)従来の内部被ばく研究では、CT画像などに基づき構築したボクセル人体ファントムを適用し、線量評価データを解析することが一般的であった。しかし、皮膚や膜状組織などをより精密に表現できるポリゴンメッシュ人体ファントムの開発が進められており、内部被ばく研究でもこのファントムを用いた評価が要求されている。しかし、モンテカルロ放射線輸送計算コードにこのファントムを取り込んで計算を行うことは、コードに精通していない場合は難しい現状となっている。そこで、PHITSの使い方に関する詳しい知識を持たないユーザーでも、このファントムを用いた内部被ばく線量計算が簡単にできるツールPARaDIMを開発した。このツールでは、グラフィカルインターフェースにより、使用する四面体メッシュファントムの選択や臓器毎の放射性核種の設定、そしてPHITSの実行が操作できる。このツールを用いた実行例をいくつか示し、先行研究との比較を行うことで、本ツールの有用性を確認した。
 Br-
Br- -methyl-phenylalanine for tumor PET imaging
-methyl-phenylalanine for tumor PET imaging花岡 宏史*; 大島 康宏; 鈴木 結利花*; 山口 藍子*; 渡辺 茂樹; 上原 知也*; 永森 收志*; 金井 好克*; 石岡 典子; 対馬 義人*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 56(5), p.791 - 797, 2015/05
被引用回数:18 パーセンタイル:62.37(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging)Radiolabeled amino acids are superior PET tracers for imaging of malignant tumors, and amino acids labeled with  Br, an attractive positron emitter due to its relatively long half-life (t
Br, an attractive positron emitter due to its relatively long half-life (t =16.2 h), could potentially be widely usable tumor imaging tracer. In this study, in consideration of stability and tumor specificity, 2-
=16.2 h), could potentially be widely usable tumor imaging tracer. In this study, in consideration of stability and tumor specificity, 2- Br-bromo-
Br-bromo- -methyl-L-phenylalanine (2-
-methyl-L-phenylalanine (2- Br-BAMP) and 4-
Br-BAMP) and 4- Br-bromo-
Br-bromo- -methyl-L-phenylalanine (4-
-methyl-L-phenylalanine (4- Br-BAMP) were designed and their potential as a tumor imaging agent was evaluated. No-carrier-added
Br-BAMP) were designed and their potential as a tumor imaging agent was evaluated. No-carrier-added  Br and
Br and  Br, the latter of which is suitable radiobromine for basic studies due to its longer half-life (t
Br, the latter of which is suitable radiobromine for basic studies due to its longer half-life (t = 57.1 h), were produced. Both
= 57.1 h), were produced. Both  Br-BAMPs were stable in the plasma and in the murine body. In biodistribution studies, 2-
Br-BAMPs were stable in the plasma and in the murine body. In biodistribution studies, 2- Br-BAMP showed more rapid blood clearance and lower renal accumulation than did 4-
Br-BAMP showed more rapid blood clearance and lower renal accumulation than did 4- Br-BAMP. More than 90% of injected radioactivity was excreted in the urine by 6 h post-injection of 2-
Br-BAMP. More than 90% of injected radioactivity was excreted in the urine by 6 h post-injection of 2- Br-BAMP. High tumor accumulation of 2-
Br-BAMP. High tumor accumulation of 2- Br-BAMP was observed in tumor-bearing mice and PET imaging with 2-
Br-BAMP was observed in tumor-bearing mice and PET imaging with 2- Br-BAMP enabled clear visualization of the tumor. These findings suggest that 2-
Br-BAMP enabled clear visualization of the tumor. These findings suggest that 2- Br-BAMP would constitute a potential new PET tracer for tumor imaging and may eventually enable the wider use of amino acid tracers.
Br-BAMP would constitute a potential new PET tracer for tumor imaging and may eventually enable the wider use of amino acid tracers.
 Br-
Br-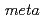 -bromobenzylguanidine
-bromobenzylguanidine渡邉 茂樹; 花岡 宏史*; Liang, J. X.; 飯田 靖彦*; 遠藤 啓吾*; 石岡 典子
Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 51(9), p.1472 - 1479, 2010/09
被引用回数:21 パーセンタイル:56.65(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging)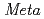 -iodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) labeled has been widely used for the diagnosis and radiotherapy of norepinephrine transporter (NET)-expressing tumors. This study demonstrated that a positron emitter
-iodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) labeled has been widely used for the diagnosis and radiotherapy of norepinephrine transporter (NET)-expressing tumors. This study demonstrated that a positron emitter  Br labeled
Br labeled 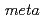 -bromobenzylguanidine (
-bromobenzylguanidine ( Br-MBBG) was prepared and evaluated as a potential PET tracer for imaging NET-expressing tumors.
Br-MBBG) was prepared and evaluated as a potential PET tracer for imaging NET-expressing tumors.  Br-MBBG was stable in vitro, but some time-dependent dehalogenation was observed after administration in normal mice. MBBG showed high uptake in PC-12 tumor cells, and this uptake was significantly decreased by the addition of NET inhibitors. In biodistribution, MBBG showed high tumor accumulation (32.0
Br-MBBG was stable in vitro, but some time-dependent dehalogenation was observed after administration in normal mice. MBBG showed high uptake in PC-12 tumor cells, and this uptake was significantly decreased by the addition of NET inhibitors. In biodistribution, MBBG showed high tumor accumulation (32.0  18.6% ID/g at 3 h p.i.) and the tumor-to-blood ratio reached as high as 54.4
18.6% ID/g at 3 h p.i.) and the tumor-to-blood ratio reached as high as 54.4  31.9. Tumor uptake of MBBG correlated very well with that of
31.9. Tumor uptake of MBBG correlated very well with that of  I-MIBG (r = 0.997), but not with
I-MIBG (r = 0.997), but not with  F-FDG. MBBG-PET showed a very clear image of the transplanted tumor with high sensitivity, and the visualized lesion was different from that by FDG-PET. These results indicated that
F-FDG. MBBG-PET showed a very clear image of the transplanted tumor with high sensitivity, and the visualized lesion was different from that by FDG-PET. These results indicated that  Br-MBBG would be a potential PET tracer for imaging NET-expressing neuroendocrine tumors, and could provide useful information for determining the indications for
Br-MBBG would be a potential PET tracer for imaging NET-expressing neuroendocrine tumors, and could provide useful information for determining the indications for  I-MIBG therapy.
I-MIBG therapy.
 Re-MAG3-conjugated bisphosphonate (
Re-MAG3-conjugated bisphosphonate ( Re-MAG3-HBP), an agent for treatment of painful bone metastases
Re-MAG3-HBP), an agent for treatment of painful bone metastases小川 数馬*; 向 高弘*; 川井 恵一*; 高村 徳人*; 花岡 宏史*; 橋本 和幸; 柴 和弘*; 森 厚文*; 佐治 英郎*
European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, 36(1), p.115 - 121, 2009/01
被引用回数:25 パーセンタイル:57.74(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging)癌性骨転移疼痛緩和に有用であるビスホスホネート骨格に安定な Re錯体を導入した
Re錯体を導入した Re-MAG3-HBPを開発してきた。一方、本薬剤の錯体形成部位MAG3と
Re-MAG3-HBPを開発してきた。一方、本薬剤の錯体形成部位MAG3と Tcとの錯体
Tcとの錯体 Tc-MAG3は、血清蛋白結合性が高く、蛋白結合阻害剤の併用により、血液及び非標的臓器からのクリアランスの促進に有効であることが示されており、本薬剤においても、同様な効果が期待される。そこで、本研究では、
Tc-MAG3は、血清蛋白結合性が高く、蛋白結合阻害剤の併用により、血液及び非標的臓器からのクリアランスの促進に有効であることが示されており、本薬剤においても、同様な効果が期待される。そこで、本研究では、 Re-MAG3-HBPの血液及び非標的臓器からのクリアランスの促進を目的に、本標識薬剤における蛋白結合阻害剤の影響を検討した。その結果、セフトリアキソンの併用により
Re-MAG3-HBPの血液及び非標的臓器からのクリアランスの促進を目的に、本標識薬剤における蛋白結合阻害剤の影響を検討した。その結果、セフトリアキソンの併用により Re-MAG3-HBPのラット血清,人血清及び人血清アルブミン中での蛋白結合率は大きく減少した。さらに、
Re-MAG3-HBPのラット血清,人血清及び人血清アルブミン中での蛋白結合率は大きく減少した。さらに、 Re-MAG3-HBPのラット体内動態におけるセフトリアキソン併用の影響を検討したところ、骨への集積性を損なうことなく、血液及び非標的臓器である肝臓,腎臓からのクリアランスが促進された。これらの結果は、蛋白結合阻害剤が、血清蛋白質と高い親和性を有する
Re-MAG3-HBPのラット体内動態におけるセフトリアキソン併用の影響を検討したところ、骨への集積性を損なうことなく、血液及び非標的臓器である肝臓,腎臓からのクリアランスが促進された。これらの結果は、蛋白結合阻害剤が、血清蛋白質と高い親和性を有する Re-MAG3-HBPの薬物動態を改善するのに有用であることを示している。
Re-MAG3-HBPの薬物動態を改善するのに有用であることを示している。
 Re-complex-conjugated bisphosphonate for the palliation of metastatic bone pain in an animal model
Re-complex-conjugated bisphosphonate for the palliation of metastatic bone pain in an animal model小川 数馬*; 向 高弘*; 浅野 大悟*; 河嶋 秀和*; 絹谷 清剛*; 柴 和弘*; 橋本 和幸; 森 厚文*; 佐治 英郎*
Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 48(1), p.122 - 127, 2007/01
転移性骨腫瘍の疼痛緩和を目的とした薬剤として、高い安定性を示す Re-MAG3錯体結合ビスホスホネート(
Re-MAG3錯体結合ビスホスホネート( Re-MAG3-HBP)を開発した。この化合物は、従来から検討されている
Re-MAG3-HBP)を開発した。この化合物は、従来から検討されている Re-HEDPに比べて、正常マウスにおいて、骨指向性薬剤として優れた体内分布を示した。
Re-HEDPに比べて、正常マウスにおいて、骨指向性薬剤として優れた体内分布を示した。 Re-MAG3-HBPの治療効果を骨転移モデル動物を用いて評価した。治療効果と副作用を評価するために、腫瘍の大きさと末梢血球数を計測し、骨痛の疼痛緩和は、機械刺激を加えるテスト法により評価した。その結果、
Re-MAG3-HBPの治療効果を骨転移モデル動物を用いて評価した。治療効果と副作用を評価するために、腫瘍の大きさと末梢血球数を計測し、骨痛の疼痛緩和は、機械刺激を加えるテスト法により評価した。その結果、 Re-HEDP投与群においては、腫瘍の大きさは未治療群と同等であった。それに対して、
Re-HEDP投与群においては、腫瘍の大きさは未治療群と同等であった。それに対して、 Re-MAG3-HBP投与群においては、有意に腫瘍増殖は抑制された。さらに、骨転移によって生じる痛みは、
Re-MAG3-HBP投与群においては、有意に腫瘍増殖は抑制された。さらに、骨転移によって生じる痛みは、 Re-MAG3-HBP又は
Re-MAG3-HBP又は Re -HEDPの投与により減弱した。しかも、その効果は、
Re -HEDPの投与により減弱した。しかも、その効果は、 Re-MAG3-HBP投与群の方が強い傾向を示した。これら結果は、
Re-MAG3-HBP投与群の方が強い傾向を示した。これら結果は、 Re-MAG3-HBPが転移性骨腫瘍の疼痛緩和薬剤として有用である可能性を示唆するものである。
Re-MAG3-HBPが転移性骨腫瘍の疼痛緩和薬剤として有用である可能性を示唆するものである。
堀内 和子*; 今野 彩*; 植田 真由美*; 福田 容子*; 西尾 早織*; 橋本 和幸; 佐治 英郎*
European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, 31(3), p.388 - 398, 2004/03
被引用回数:21 パーセンタイル:50.16(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging)腫瘍骨転移には造骨性と溶骨性があり、その鑑別診断を行うことが治療の際に重要であり、これまでの研究成果からビスホスホネート化合物( Tc,
Tc,  Re-BP)は造骨性骨腫瘍に集積し、ジメルカプトコハク酸化合物(
Re-BP)は造骨性骨腫瘍に集積し、ジメルカプトコハク酸化合物( Tc,
Tc,  Re(V)-DMS)は溶骨性骨転移部位への集積が報告されている。本研究では、溶骨性骨転移部位へ集積するジメルカプトコハク酸化合物の集積機構を詳細に検討した。
Re(V)-DMS)は溶骨性骨転移部位への集積が報告されている。本研究では、溶骨性骨転移部位へ集積するジメルカプトコハク酸化合物の集積機構を詳細に検討した。 Tc(V)-DMS及び
Tc(V)-DMS及び Re(V)-DMSの溶骨性骨転移部位への集積には破骨細胞が関与していると考えられる。破骨細胞は低pH時に高い骨吸収活性を示すことから、グルコース投与により酸性症を発現したマウスを使用した動物実験及び細胞取り込み実験に対するpH効果を調べた。その結果、細胞内の酸性化がDMS化合物の取り込みに関与することが示唆された。溶骨性骨腫瘍は破骨細胞の活性化と局所的な細胞外液の酸性化を伴うことから、
Re(V)-DMSの溶骨性骨転移部位への集積には破骨細胞が関与していると考えられる。破骨細胞は低pH時に高い骨吸収活性を示すことから、グルコース投与により酸性症を発現したマウスを使用した動物実験及び細胞取り込み実験に対するpH効果を調べた。その結果、細胞内の酸性化がDMS化合物の取り込みに関与することが示唆された。溶骨性骨腫瘍は破骨細胞の活性化と局所的な細胞外液の酸性化を伴うことから、 Tc(V)-DMSの溶骨性骨腫瘍の診断及び
Tc(V)-DMSの溶骨性骨腫瘍の診断及び Re(V)-DMSの溶骨性骨転移の疼痛緩和における有効性(可能性)が示された。
Re(V)-DMSの溶骨性骨転移の疼痛緩和における有効性(可能性)が示された。
 Re-labeled monoclonal antibody
Re-labeled monoclonal antibody絹谷 清剛*; 横山 邦彦*; 久藤 美保*; 笠原 善仁*; 小林 勝利; 本石 章司; 小野間 克行; 分校 久志*; 道岸 隆敏*; 利波 紀久*
Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 42(4), p.596 - 600, 2001/04
正常p53遺伝子の欠けた腫瘍細胞は、電離放射線照射によるDNA障害を受けると細胞周期のG2期において停止し、その障害を修復することにより、放射線耐性を示す。methylxanthine誘導体がG2停止を阻害し、放射線増感効果を示すことが知られているものの、放射性アイソトープによる低線量率 線照射に対する影響に関する情報は乏しいのが現状である。本研究の目的は、
線照射に対する影響に関する情報は乏しいのが現状である。本研究の目的は、 線照射に対するmethylxanthine誘導体の効果を観察し、内照射療法への応用の可否を検討することにある。LS180ヒト大腸癌細胞を、
線照射に対するmethylxanthine誘導体の効果を観察し、内照射療法への応用の可否を検討することにある。LS180ヒト大腸癌細胞を、 Re-MAG3あるいは
Re-MAG3あるいは Re-MAG3標識大腸癌A7抗体(0~25
Re-MAG3標識大腸癌A7抗体(0~25 Ci/ml)により、pentoxifyllineあるいはCaffeineの存在下に照射し、細胞生存曲線を得て、methylxanthine誘導体による効果比を算出した。対照として、高線量率X線照(0~4Gy,1.4Gy/min)における効果比と比較した結果、
Ci/ml)により、pentoxifyllineあるいはCaffeineの存在下に照射し、細胞生存曲線を得て、methylxanthine誘導体による効果比を算出した。対照として、高線量率X線照(0~4Gy,1.4Gy/min)における効果比と比較した結果、 Reの
Reの 線の殺細胞効果が大きい可能性がある。
線の殺細胞効果が大きい可能性がある。